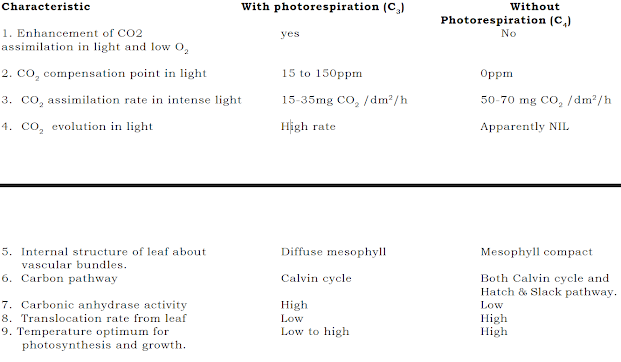
Photorespiration is a special type of respiration shown by many green plants when they are exposed to light. The normal dark respiration (usual mitochondrial respiration) is independent of light and its rate is the same in both light and dark. The photorespiration process is carried on only in the presence of light. The term photorespiration is referred to as “ the release of CO2 in respiration in presence of light during photosynthesis”. Importance of Photorespiration a. Photorespiration is closely related to the CO2 compensation point. b. It usually occurs only in those plants, which have comparatively high CO2 compensation points. (eg. Tomato, wheat, oats, etc.) c. It is insignificant or rather absent in C4 plants, which have very low CO2 compensation points] (eg. maize, sugarcane, sorghum, pearl millet, amarantus, etc.).