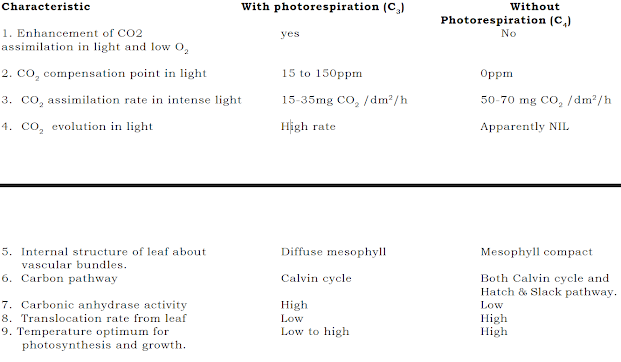
Significance of Photorespiration in Crop-Productivity
1. Often, the presence of photorespiration is considered a wasteful and energy-consuming process in crop plants which ultimately leads to a reduction in the final yield of crops.
2. It is estimated that during C3 photosynthesis, up to 50% of the CO2 fixed may have to pass through the photorespiratory process (glycolate pathway) to form carbohydrates such as sucrose thereby resulting in a considerable decrease in photosynthetic productivity.
3. Unlike usual mitochondrial respiration, assimilatory powers (ATP or NADPH2 ) are not generated in photorespiration.
4. However, photorespiration is considered as a metabolic adjunct to the Calvin cycle (i.e., it has been added to the Calvin cycle but essentially it is not a part of the C3 cycle).
5. Because the photorespiration process decreases the photosynthetic efficiency of crop plants, scientists are working to increase the efficiency of C3 plants by decreasing photorespiration.
5.1 Ways to reduce the effect of photorespiration would be :
a. to increase the CO2 concentration, and
b. to develop varieties or strains of C3 plants, which have a low photorespiration rate.
Comments
Post a Comment